CATARACT


Problems with cataract include-
- Cloudy, blurred or dim vision
- Increasing difficulty with vision at night
- Increased sensitivity to light.
- Glare
- Need for brighter light for reading and other activities
- Seeing “halos” around lights
- Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription
- Fading or yellowing of colors
- Double vision in a single eye

RISK FACTORS
- Aging
- Associated ocular conditions
- Myopia (it is when the eye is not able to focus properly on obects in distance)
- Retinal detachment (the retina separates from the layer underneath)
- Infection
- Aspirin
- Corticosteroids
- Cigarette smoking
- Chemical burns
- Ionizing radiation
- Poor nutrition
- Blunt trauma
- Ultraviolet radiation in sunlight and x-ray
- Diabetes
- Renal disorders
- Musculoskeletal disorders
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Snellen visual acuity testing
Ophthalmoscopy
Slit lamp examination
TREATMENT
Cloudy lens needs a Replacement with a clear lens by means of surgery
Cataract Surgery – Key Points:
- Quick and safe outpatient procedure
- Usually takes 15–30 minutes
- Fast recovery (few days to weeks)
- Vision improves gradually after surgery
- Eye drops are used for healing and to prevent infection

- LASER CATARACT SURGERY
- MICS IOL
- PHACO IOL
Phacoemulsification with intra ocular Lens Implantation has been the most accepted and successful treatment for Cataracts worldwide. Cloudy Lens is removed from the eye through a tiny opening and a foldable artificial lens is implanted into the eye.
Types of Intraocular Lenses (IOLs)
1. Monofocal IOL
- Description: Standard lens that provides clear vision at one distance (usually far).
- Note: You may still need glasses for reading or close-up work.
2. Multifocal IOL
- Description: Designed to provide vision at multiple distances (near, intermediate, and far).
- Note: May reduce the need for glasses but can cause halos or glare, especially at night.
3. Extended Depth of Focus (EDOF) IOL
- Description: Provides a continuous range of vision (especially distance and intermediate).
- Note: Less glare and halos than multifocal lenses but may still require reading glasses.
4. Toric IOL
- Description: Corrects astigmatism along with cataract.
- Note: Customized for patients with corneal astigmatism.
5. Accommodative IOL
- Description: Mimics natural lens movement to shift focus between near and far.
- Note: Mixed results in near vision correction; often combined with reading glasses.
6. Light-Adjustable IOL (LAL)
- Description: Post-surgery, lens power can be fine-tuned using UV light for optimal vision.
- Note: Requires special post-op light treatments but offers customizable vision outcomes.
Post-Surgery Do’s and Don’ts:
Do’s: ✅ Use prescribed eye drops
✅ Wear protective eye shield/glasses
✅ Keep your eye clean
Dont’s: ❌ Don’t rub your eye
❌ Don’t lift heavy objects
❌ Avoid swimming or dusty environments
SPECTACLE REMOVAL WITH ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & LASIK
👁️ Tired of glasses or contact lenses?
Modern eye care offers advanced laser vision correction techniques like LASIK, helping you enjoy clear, natural vision—without glasses!
🔍 What is LASIK?
LASIK (Laser-Assisted In Situ Keratomileusis) is a safe, quick, and effective laser eye surgery that reshapes the cornea to correct:
- Nearsightedness (Myopia)
- Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
- Astigmatism
It offers freedom from glasses or contact lenses for many patients.

🛠️ Advanced Technologies Used:
- Femto-LASIK (Blade-Free LASIK)
- Uses a femtosecond laser for flap creation – safer, more precise
- Reduced discomfort and faster healing
- Contoura Vision (Topography-Guided LASIK)
- Customizes treatment based on your eye’s unique shape
- Offers superior clarity and better quality of vision than standard LASIK
- SMILE (Small Incision Lenticule Extraction)
- Minimally invasive
- No flap – suitable for active lifestyles and dry eye patients
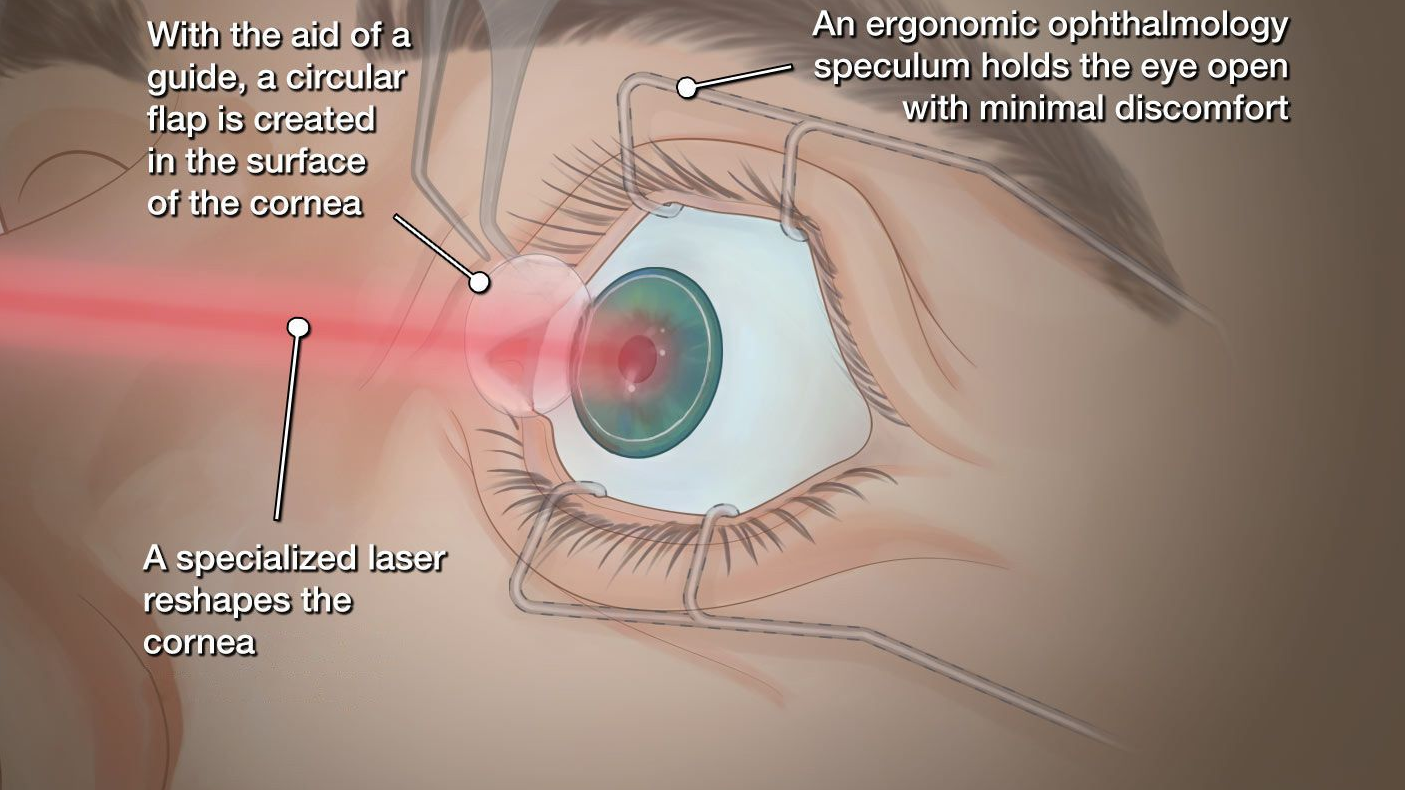
⏱️ Procedure Overview:
- Done in 10–15 minutes per eye
- Painless, with numbing eye drops
- Clear vision within 24–48 hours
- Back to work or normal activities in 1–2 days
✅ Benefits:
- Clear vision without glasses or lenses
- Long-lasting results
- Fast recovery
- Safe and precise with modern technology
👤 Who Can Have LASIK?
- Age 18+ with stable vision
- Healthy eyes (no cataract, glaucoma, or severe dry eye)
- Not pregnant or breastfeeding
👉 A detailed eye exam will determine if you’re a good candidate.
⚠️ Possible Side Effects (Usually Temporary):
- Dry eyes
- Light sensitivity
- Glare or halos at night
🕶️ Aftercare Tips:
- Use prescribed eye drops
- Avoid eye rubbing
- Wear sunglasses
- Attend follow-up visits
PTERYGIUM SURGERY
Pterygium is a non-cancerous growth on the white part of the eye that can slowly grow onto the cornea. It often appears as a pink, triangle-shaped tissue, usually near the nose.
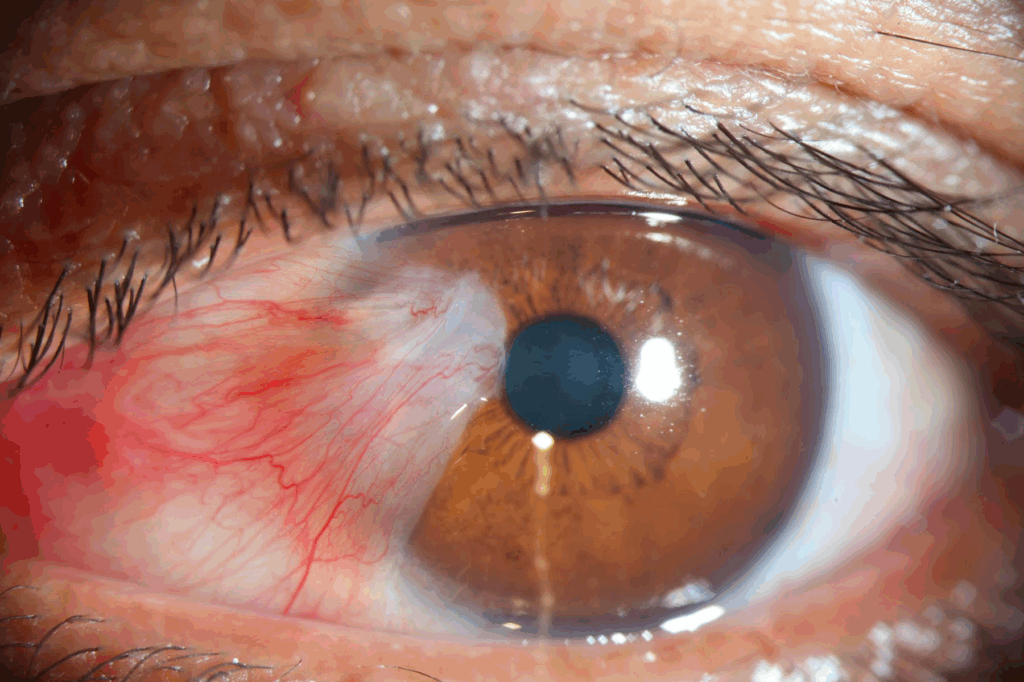
🌞 Causes:
- Sunlight (UV exposure)
- Dust, wind, dry air
- Common in people who spend time outdoors
⚠️ Symptoms:
- Redness or irritation
- Dry or gritty feeling
- Blurred vision (if it grows over the cornea)
- Cosmetic concern
🩺 Treatment:
- Eye drops for irritation
- Surgery if it affects vision or causes discomfort
- UV-protective sunglasses help prevent growth or recurrence
🛠️ Types of Pterygium Surgeries:
1. Bare Sclera Technique
- The pterygium is removed, and the area is left uncovered.
- Simple and quick, but has a higher chance of coming back (recurrence).
2. Conjunctival Autograft
- After removal, a piece of your own healthy conjunctiva (from another part of your eye) is used to cover the area.
- Lower recurrence rate than bare sclera.
- May be done with stitches or glue.
3. Amniotic Membrane Graft
- Instead of your own tissue, a donated amniotic membrane is used to cover the area.
- Helps with healing and reducing inflammation.
- Useful for large or recurrent pterygium cases.
4. Use of Anti-Scarring Medications (e.g., Mitomycin-C)
- Sometimes used during surgery to reduce recurrence.
- May be combined with other techniques.
📌 See a Doctor If:
- It’s growing
- Your vision changes
- You feel ongoing discomfort
IMPLANTABLE COLLAMER LENS
ICL is a soft, permanent lens implanted inside the eye to correct vision problems like nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism. It works with your natural lens and is invisible, reversible, and safe.
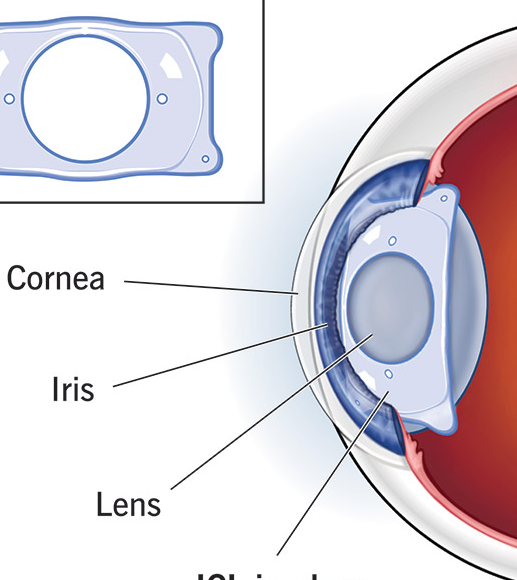
✅ Benefits:
- Clear, sharp vision
- Quick recovery (1–2 days)
- UV protection built-in
- Suitable for people who can’t have LASIK
- Doesn’t remove corneal tissue
- Can be removed if needed
👤 Good Candidates:
- Age 21–45
- Stable vision
- Not ideal for LASIK (thin cornea, dry eyes)
🩺 Procedure Overview:
- Painless, outpatient surgery
- Takes ~20–30 minutes
- One eye at a time
- Use eye drops after surgery
- Vision improves quickly
🗓️ Follow-Up Care:
- First visit 1–2 days after surgery
- Regular check-ups to monitor eye health
RETINAL SERVICES
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
Diabetic Retinopathy is an eye disease caused by diabetes. High blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina (the part of the eye that senses light), which can lead to vision problems and even blindness if not treated early.

🔍 Who is at Risk?
- Pregnant women with diabetes
- People with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes
- Poor blood sugar control
- Long-standing diabetes (more than 5 years)
- High blood pressure or high cholesterol
⚠️ Symptoms (Often No Early Signs):
- Blurry or fluctuating vision
- Dark spots or floaters
- Poor night vision
- Sudden loss of vision (in advanced cases)

Important: You may not notice symptoms until the disease is advanced — that’s why regular eye exams are crucial.
🩺 Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Mild to Moderate Non-Proliferative DR – early damage; may have no symptoms
- Severe Non-Proliferative DR – more bleeding and blocked vessels
- Proliferative DR – new, abnormal blood vessels grow and may bleed, leading to vision loss
- Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) – swelling in the central retina, affecting sharp vision
✅ How Is It Treated?
- Good blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol control
- Laser treatment – seals leaking vessels
- Anti-VEGF injections – reduce swelling and abnormal blood vessels
- Vitrectomy surgery – removes blood or scar tissue in advanced cases
👁️🗨️ Prevention & Eye Care Tips:
- Control your blood sugar, BP, and cholesterol
- Quit smoking
- Have a dilated eye exam at least once a year
- Report any vision changes immediately
🗓️ Remember:
Diabetic Retinopathy can be managed and vision can be saved—but early detection is key.
ARMD

Age-Related Macular Degeneration (ARMD or AMD) is an eye disease that affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. It can cause blurred or distorted central vision, making it hard to read, drive, or recognize faces.
👤 Who is at Risk?
- Age 50 and above
- Family history of ARMD
- Smoking
- High blood pressure or cholesterol
- Poor diet or lack of antioxidants
- Sunlight (UV) exposure without protection
🔍 Types of ARMD:
- Dry ARMD (Common form)
- Gradual breakdown of the macula
- Slower vision loss
- Wet ARMD (Less common but more serious)
- Abnormal blood vessels grow under the retina and leak fluid or blood
- Can lead to sudden, severe vision loss
⚠️ Symptoms:
- Blurred or fuzzy vision
- Straight lines appear wavy (metamorphopsia)
- Difficulty seeing in low light
- Blank or dark spots in the center of vision
🩺 Diagnosis:
- Comprehensive dilated eye exam
- OCT scan to view retina layers
- Fluorescein angiography (for wet ARMD)
✅ Treatment Options:
For Dry ARMD:
- No cure, but progression can be slowed
- AREDS2 vitamins (antioxidant supplements)
- Healthy diet: green leafy vegetables, fish, nuts
- Regular monitoring with an Amsler grid
For Wet ARMD:
- Anti-VEGF injections to stop abnormal blood vessel growth
- Sometimes combined with laser treatment and surgery
🌞 Prevention & Eye Health Tips:
- Quit smoking
- Eat a diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3s, and leafy greens
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol
- Wear UV-protective sunglasses
- Get regular eye check-ups, especially after age 50
📌 Important:
ARMD does not cause complete blindness, but it can severely affect central vision.
Early detection and treatment can preserve your sight.
RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA
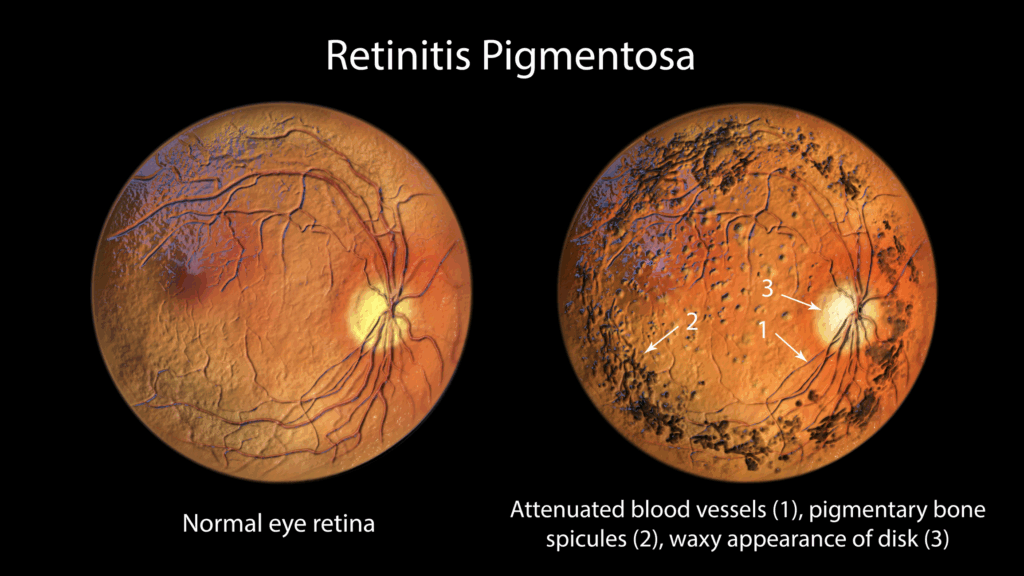
Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) is a genetic eye disease that causes gradual vision loss, affecting your night vision and side vision. It may eventually lead to severe vision loss.
⚠️ Symptoms:
- Difficulty seeing in the dark (night blindness)
- Loss of side (peripheral) vision
- Tunnel vision (narrow field of view)
- Sensitivity to light
🧬 Causes:
RP is inherited and caused by changes in the genes that affect the retina, the light-sensitive part of the eye.
🩺 Diagnosis:
- Eye exam and visual field test
- Electroretinogram (ERG) to check retinal function
✅ Treatment & Management:
- No cure yet, but management focuses on maximizing remaining vision
- Low vision aids (magnifiers, special glasses)
- Vitamin A supplements (under doctor’s advice)
- Gene therapy (research ongoing)
📌 Tips for Living with RP:
- Use brighter lighting
- Wear UV-protective sunglasses
- Stay active with mobility training
- Regular eye exams are essential
Although RP leads to progressive vision loss, early management can help you maintain independence.
MACULAR HOLE
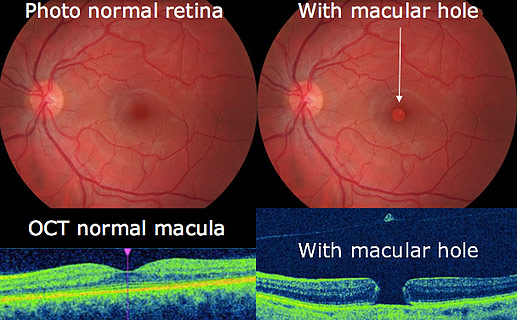
A macular hole is a small tear in the macula (the central part of the retina), causing blurred or distorted central vision.
⚠️ Causes:
- Often caused by age-related changes in the eye
- Can also result from eye trauma or previous eye surgery
👁️ Symptoms:
- Blurred or wavy central vision
- Dark spot in the center of vision
🩺 Diagnosis:
- Eye exam and OCT scan for detailed retinal images
✅ Treatment:
- Observation for small holes
- Vitrectomy surgery (removes vitreous gel and places a gas bubble) for larger holes
- Head positioning after surgery helps healing
📌 Note:
Early treatment can improve vision, but it may not return to normal. Regular follow-up is important.
MACULAR EDEMA
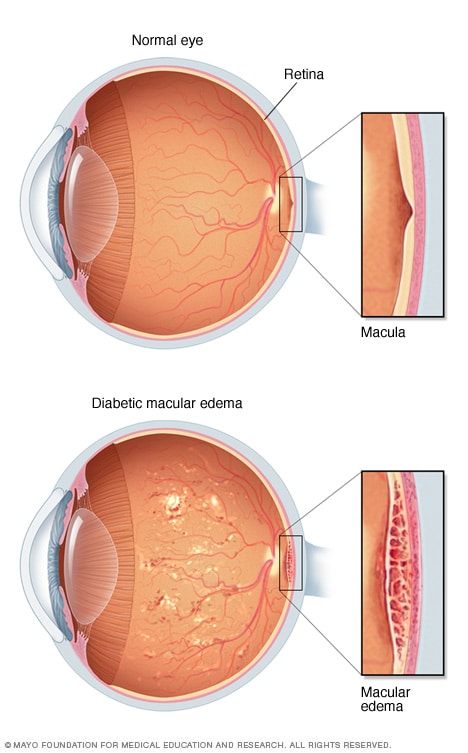
Macular edema is the swelling of the macula (central retina), causing blurred or distorted vision.
⚠️ Causes:
- Diabetes (most common)
- Retinal vein blockage
- Eye surgery or trauma
- Eye inflammation (uveitis)
👁️ Symptoms:
- Blurred or distorted central vision
- Difficulty seeing fine details
🩺 Diagnosis:
- Eye exam and OCT scan to check the retina
✅ Treatment:
- Anti-VEGF injections or steroids
- Laser treatment
- Manage underlying conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure
📌 Note:
Early detection and treatment can help prevent vision loss and replace it with a clear solution.
RETINAL DETACHMENT
Retinal detachment occurs when the retina pulls away from the back of the eye, which can lead to vision loss if untreated.

⚠️ Causes:
- Age-related changes
- Eye injury or trauma
- Eye diseases like diabetic retinopathy
👁️ Symptoms:
- Flashes of light
- Floaters (dark spots)
- Blurred or shadowed vision
- Curtain-like shadow across vision
🩺 Diagnosis:
- Eye exam and retinal imaging
✅ Treatment:
- Laser surgery or cryotherapy
- Vitrectomy or scleral buckle surgery for reattaching the retina
📌 Note:
Retinal detachment is a medical emergency—seek treatment immediately to protect your vision.
GLAUCOMA SERVICES

The increased eye pressure, called intra-ocular pressure, can damage the optic nerve of the eye , which transmits images to your brain. If the damage continues, glaucoma can lead to permanent vision loss. Without treatment, glaucoma can cause total permanent blindness within a few years.

SYMPTOMS OF GLAUCOMA :
- Severe throbbing eye pain
- Redness of eye
- Headache (on the same side as the affected eye)
- Blurry or foggy vision
- Seeing ” Halos” around lights,
- Fixed Mid-Dilated pupil
- Nausea and Vomiting

INVESTIGATIONS AND TREATMENT MODALITIES :
1.PERIMETRY- Humphrey feild analyser
2. OCT
3. YAG LASER
4. UBM
5. SURGERY
Glaucoma is a life-long condition and needs a longer follow-up with your eye doctor.
1. Eye Drops (First-Line Treatment)
Used to lower eye pressure.
- Prostaglandin analogs – increase fluid drainage (e.g., latanoprost)
- Beta-blockers – reduce fluid production (e.g., timolol)
- Alpha agonists – decrease fluid and increase drainage
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors – lower fluid production
- Rho kinase inhibitors – newer drops to increase outflow
👉 Take them daily as prescribed – never skip doses!
2. Oral Medications
- Used when eye drops aren’t enough (e.g., acetazolamide)
- Short-term use due to side effects
3. Laser Treatments
- Laser trabeculoplasty (SLT/ALT): helps fluid drain out of the eye
- Laser iridotomy: used in angle-closure glaucoma
✅ Quick, outpatient, often painless
4. Surgical Procedures
When drops and lasers aren’t enough:
- Trabeculectomy: creates a new drainage path
- Glaucoma drainage implants: tube placed to help fluid drain
- Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS): safer, quicker recovery, often combined with cataract surgery
UVEAL DISORDERS
Uveitis is a form of eye inflammation. It affects the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall (uvea). Uveitis (u-vee-I-tis) warning signs often come on suddenly and get worse quickly. They include eye redness, pain and blurred vision

The signs, symptoms and characteristics of uveitis may include:
SYMPTOMS
- Eye redness
- Eye pain
- Light sensitivity
- Blurred vision
- Dark, floating spots in your field of vision (floaters)
- Decrease vision
TREATMENT
- Prescription eye drops in combination with anti-inflammatory medications
- Ocular anti-inflammatory injections – injections may be to the outside or inside of the eye
- Systemic or oral administration of steroids, other immunosuppressant or anti-metabolite drugs
CONTACT LENS CARE
Contact lenses are thin, curved lenses placed directly on the surface of the eye to correct vision. They are an alternative to eyeglasses and can be used to treat conditions like nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia.
🧾 Types of Contact Lenses:
- Soft Contact Lenses – comfortable and flexible; most commonly used
- Daily, bi-weekly, or monthly disposables
- Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lenses – durable, offer sharper vision for some conditions
- May take time to get used to
- Toric Lenses – designed for astigmatism
- Multifocal Lenses – help with both near and distance vision (for presbyopia)
- Colored/ Cosmetic Lenses – change eye color; should be used carefully and hygienically
🧼 Proper Care & Hygiene:
- Wash hands before handling lenses
- Use only prescribed solutions (never water or saliva)
- Clean and store lenses as directed
- Replace lenses and cases regularly
- Never sleep in lenses unless approved
- Avoid wearing them while swimming or in dusty environments
⚠️ Watch for These Warning Signs:
- Redness or pain in the eye
- Blurry vision
- Discharge
- Sensitivity to light
👉 If any of these occur, remove lenses immediately and see your eye doctor.
✅ Tips for Safe Use:
- Follow wearing schedule
- Don’t share lenses
- Get regular eye checkups
- Always have a backup pair of glasses
Contact lenses are safe, convenient, and effective when used properly. Follow your eye care provider’s instructions for the best results and healthy eyes.
CORNEAL ULCER TREATMENT
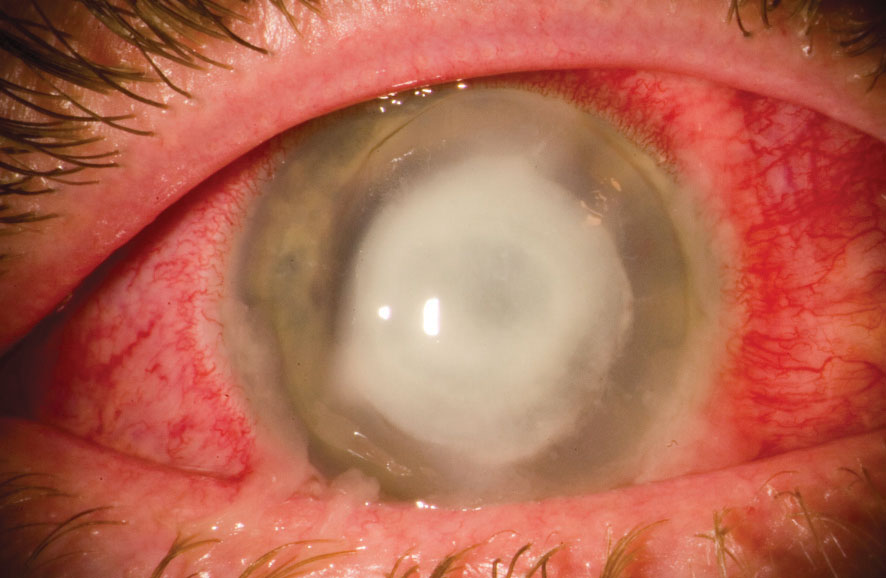
CORNEAL SCRAPING -where a portion of ulcer removed with help of blade locally to find out causitive organism.
CORNEAL DEBRIDEMENT -where ulcer as a whole is removed topically and investigated further to find out cause.
THERAPEUTIC PENETRATING KERATOPLASTY
WANT A CURE FOR NON RESPONDING ULCERS?
Therapeutic Penetrating Keratoplasty is a surgical procedure where diseased cornea is replaced with healthy donor cornea.
KERATOCONUS MANAGEMENT WITH RECENT TECHNOLOGY
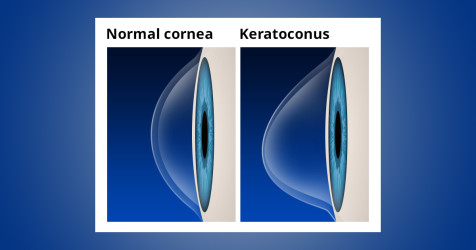
Keratoconus is a condition in which normal shape of cornea becomes conical.
It is generally observed in :
Those having high cylindrical power
Progressive change in spectacle power
Family History positive
Who Are at RISK ?
HOW DO WE COME TO KNOW ?

HOW DO WE GET RID OF THAT?
CORNEAL COLLAGEN CROSSLINKING PROCEDURE(C3R) : Procedure where transparent portion cornea is treated with riboflavin drops after removing superficial layer followed by exposure to ultraviolet radiation. It is a painless procedure.

